A Complete Beginner’s Guide to Japan’s Import Declaration System, Required Documents, Costs, Duties, Tax Rates, and Common Issues
- Introduction
- 1. What Is NACCS?
- 2. Basics of Import Customs Clearance in Japan
- 3. Import Declaration Flow Using NACCS (Illustrated)
- 4. Documents Required for Import Declaration
- 5. How Customs Duties and Consumption Tax Are Calculated
- 6. Costs Associated with Using NACCS
- 7. Common Problems and How to Avoid Them
- 8. What Is an Importer Code?
- 9. Key Takeaways for Import Declarations
- Reference Materials
Introduction
When importing goods into Japan from overseas, one procedure is unavoidable: import customs clearance (import declaration).
Today, the majority of these customs procedures are handled electronically through NACCS (Nippon Automated Cargo and Port Consolidated System).
This article provides a clear and practical explanation for beginners, covering:
- What NACCS is and whether foreign importers need to use it
- The overall structure of import declarations in Japan
- Required documents, duties, tax rates, and costs
- Common problems and how to prevent them
1. What Is NACCS?
NACCS (Nippon Automated Cargo and Port Consolidated System) is Japan’s dedicated online system for customs clearance and port-related procedures. It connects Japan Customs with other government authorities, customs brokers, importers/exporters, shipping lines, airlines, and logistics providers.
In Simple Terms
NACCS is a shared electronic platform used by:
- Japan Customs
- Relevant government agencies
- Licensed customs brokers
- Importers and exporters
- Shipping lines and air carriers
Processes that previously required paper documents and in-person visits to customs offices are now handled digitally, resulting in:
- Greater procedural efficiency
- Reduced risk of clerical errors
- Shorter clearance lead times
What You Can Do with NACCS
- Import declarations to Japan Customs
- Export declarations
- Vessel and aircraft arrival/departure notifications
- Status tracking of customs procedures
- Management of tariff quotas and related controls
Understanding where NACCS fits within the overall import process helps prevent delays and errors.
2. Basics of Import Customs Clearance in Japan
What Is Import Customs Clearance?
Import customs clearance is the process by which an importer declares to Japan Customs:
- Product description, quantity, and customs value (FOB/CIF basis)
- Country of origin (COO)
- Importer and declarant information
After duties, consumption tax, and other applicable taxes are paid, the goods are legally released into the Japanese market.
Overview of the Customs Clearance Process
- Cargo arrives in Japan and is transferred to a bonded area
- Import declaration is submitted via NACCS
- Documentary review and, if required, physical inspection
- Calculation and payment of customs duties and taxes
- Import permit is issued
- Goods are released from the bonded area and delivered domestically
A bonded area is a designated location where goods may be stored before duties and taxes are paid.
3. Import Declaration Flow Using NACCS (Illustrated)
Below is a simplified flow that is easy for beginners to understand:
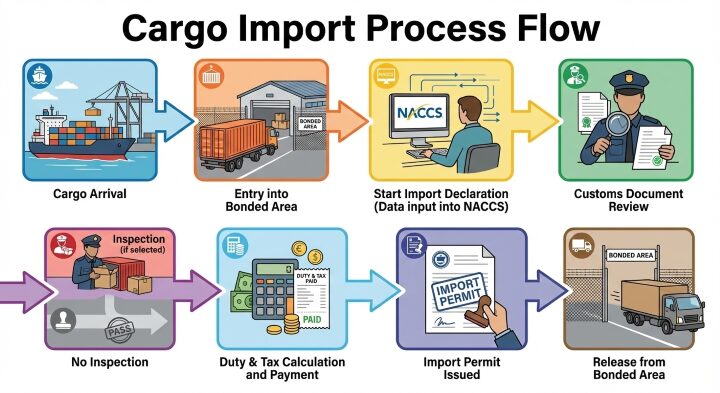
Because the process is electronic, handwritten paperwork is rarely required.
4. Documents Required for Import Declaration
In NACCS, the following information and documents must be entered or attached.
✔ Mandatory Documents and Information
| Document / Information | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Commercial Invoice | Declares transaction value and Incoterms (FOB, CIF, etc.) |
| Bill of Lading (B/L) or Air Waybill | Confirms transport details and carrier |
| Packing List | Details contents and packaging |
| Quantity, Value, Country of Origin | Basis for customs duty calculation |
| Importer Information (name, address, importer code) | Required for NACCS filing |
From October 2025 onward, additional data related to e-commerce platforms must also be declared.
✔ Documents Required Depending on the Case
- Certificate of Origin (for preferential tariff treatment under FTAs)
- Import licenses or approvals (for regulated goods such as food, pharmaceuticals, or chemicals)
- Other regulatory documents (e.g., quarantine or sanitary certificates)
For a comprehensive understanding of food import procedures and quarantine requirements, see MAFF Basics of Food Import & Quarantine
You might also find this article helpful.
→ Certificates of Origin for Food Imports: Complete Guide for Importers
→ Common Quarantine Issues in Food Imports and How to Handle Them | Food-Specific Checklist Included
5. How Customs Duties and Consumption Tax Are Calculated
Customs Duties
Customs duties are determined based on the HS code classification of the goods.
Duty rates vary depending on:
- Product classification (HS code)
- Country of origin
- Applicable trade agreements
Calculate import duties accurately and consider preferential tariffs using the resources from Japan Customs and JETRO FTA/EPA Guide
Consumption Tax
Imported goods are subject to Japanese consumption tax (standard rate: 10%).
Reduced rates may apply to certain items such as food and beverages.
🧮 Other Applicable Taxes
Depending on the product, additional taxes may apply, including:
- Liquor tax
- Petroleum and energy-related taxes
For more information, see this article.
→ How to Find HS Codes for Beginners: 3 Common Mistakes to Avoid
→ How to Legally Reduce Customs Duties and Consumption Tax on Food Imports
6. Costs Associated with Using NACCS
Although NACCS itself is a government-operated system, importers typically incur costs such as:
- NACCS usage arrangements
- Communication systems and software
- Customs broker service fees
Typical Cost Items
| Cost Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Customs broker fees | Charged when declarations are filed by a licensed broker |
| NACCS system fees | System connection fees borne by brokers or service providers |
| Non-tax charges | Container devanning, bonded storage, warehouse fees |
Most importers outsource the entire declaration process to a customs broker.
7. Common Problems and How to Avoid Them
❗ Issue ① Incomplete or Incorrect Documents
Errors or missing documents can stop the review process and delay cargo release.
Common cause: Mismatch between the invoice and NACCS declaration data.
Prevention: Double-check all data before submission.
❗ Issue ② Incorrect HS Code Classification
Misclassification leads to incorrect duty rates and potential back taxes.
Solution: Use Japan Customs’ advance ruling system for complex products.
❗ Issue ③ Failure to Comply with Regulatory Requirements
Missing approvals for regulated items (e.g., food, pharmaceuticals) can result in delays or re-export.
Prevention: Prepare documentation in line with relevant laws, such as food sanitation or quarantine regulations.
For a full English version of Japan’s food safety law, refer to the official Food Sanitation Act translation at the Japanese Law Translation website: https://www.japaneselawtranslation.go.jp/en/laws/view/5024. This outlines basic safety, labeling, additive controls, and inspection provisions that apply to imported food.
8. What Is an Importer Code?
An Importer Code is a unique identification number used in NACCS declarations to identify the importer.
💡 How to Obtain One
- Corporations: The corporate number is generally used
- Individuals: If no corporate number exists, an importer code is issued by Japan Customs upon application
9. Key Takeaways for Import Declarations
✔ Import declarations in Japan are fundamentally data-driven through NACCS
✔ Accuracy and completeness of documents are critical
✔ Customs duties and consumption tax are calculated automatically based on HS codes
✔ Broker fees and ancillary charges should be reviewed carefully
✔ Preventive checks significantly reduce clearance errors
NACCS is the core system for import declarations in Japan. Understanding when and how it is used within the overall logistics flow—especially for food imports subject to additional inspections—ensures smoother and faster clearance.
Additional Insights
- Do foreign importers need to use NACCS?
Foreign companies typically do not access NACCS directly; instead, licensed Japanese customs brokers file declarations on their behalf. - How are food imports cleared in Japan?
Food imports require coordination between NACCS, Japan Customs, and food sanitation authorities, with inspection results electronically linked to the import declaration process.